Social and Economic Indicators
Economic and social indicators can be used to measure socioeconomic development of the society by having indicators such as GDP, GVA (gross value added), unemployment level, life expectancy, education level, crime and safety, and level of participation in civil society.
Social and economic indicators are essential metrics used to assess the well-being and development of a society or economy. These indicators provide insights into various aspects of a nation’s or region’s health, prosperity, and overall quality of life. Here are some common social and economic indicators:
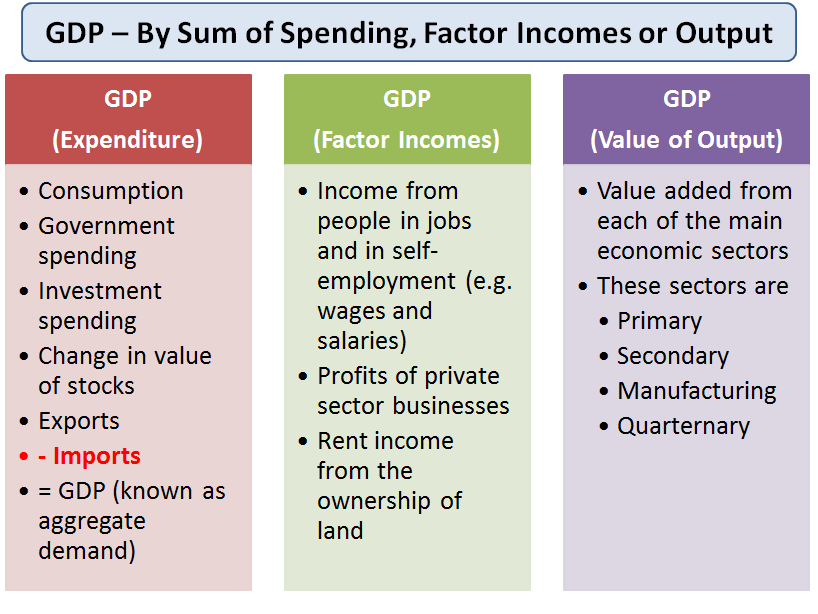
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): GDP measures the total economic output of a country or region. It is often used as a primary indicator of economic performance and growth.
- Unemployment Rate: This indicates the percentage of the labor force that is currently unemployed and seeking employment. It’s a crucial measure of economic health.
- Inflation Rate: Inflation measures the increase in the prices of goods and services over time. It affects the purchasing power of a currency.
- Poverty Rate: This indicator reflects the percentage of the population living below the poverty line, typically defined as a certain income level necessary to meet basic needs.
- Human Development Index (HDI): The HDI combines indicators like life expectancy, education, and per capita income to provide a comprehensive measure of a country’s development.
- Income Inequality: Metrics like the Gini coefficient or income quintile ratios measure the distribution of income within a population, highlighting disparities between rich and poor.
- Education Attainment: This includes indicators like literacy rates, school enrollment ratios, and the average number of years of schooling.
- Healthcare Access: Metrics related to healthcare include the availability of healthcare services, life expectancy, and disease prevalence.
- Labor Force Participation Rate: This measures the percentage of the working-age population that is actively engaged in the labor market.
- Environmental Sustainability Indicators: These indicators focus on environmental factors such as carbon emissions, renewable energy use, and natural resource conservation.
- Quality of Life Index: This is a composite indicator that considers factors like safety, healthcare, education, and other aspects contributing to overall well-being.
- Social Capital: This concept encompasses trust, social cohesion, and community involvement, which can influence a society’s economic and social outcomes.
These indicators are used by governments, policymakers, researchers, and organizations to make informed decisions, monitor progress, and address challenges in areas related to social and economic development. The specific indicators of interest can vary depending on the context and the goals of the analysis or policy objectives.
Economic Indicators: Your Economic Compass
Imagine you’re on a hike, and the only way to know which way to go is by looking at the landscape: mountains tell you about altitude, rivers show directions, and trees indicate wind patterns. Economic indicators are similar – they’re data points that help us understand the health and direction of the economy.
Think of them as the economy’s weather forecast. Some key indicators include:
- GDP: This is like the total size of the economy, telling us how much stuff (goods and services) is being produced.
- Unemployment rate: This shows how many people are looking for work, giving us a sense of job availability.
- Inflation rate: This measures how prices change over time, indicating how expensive things are getting.
- Interest rates: These are the costs of borrowing money, affecting things like mortgages and business loans.
By following these and other indicators, we can:
- See how the economy is doing right now: Are we growing, stable, or shrinking?
- Make predictions about the future: Will there be more jobs? Will prices rise?
- Make informed decisions: Should you invest in a business? Should you save more money?
Economic indicators aren’t perfect, but they’re like having a compass on your economic hike – they help you navigate the ups and downs and make informed choices.
Remember, the key is to keep it simple: Indicators are just data points that tell us about the economy’s health and direction. With this understanding, you can use them to make better decisions in your own life and stay ahead of the economic curve.
